Your specialist for parallel keys …
Give us a call. We will be pleased to advise you.
fon: +49 (0)2391 91796–0
fax: +49 (0)2391 91796–30
Your specialist for parallel keys …
Give us a call. We will be pleased to advise you.
fon: +49 (0)2391 91796–0
fax: +49 (0)2391 91796–30
Tangential Keys
Key Details About Our Tangential Keys
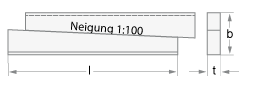
Available Dimensions
| Calculated key height | h | 19.3 – 157.1 mm |
| Thickness | t | 7.0 – 42.0 mm |
| Length | l | 50.0 – 400.0 mm |
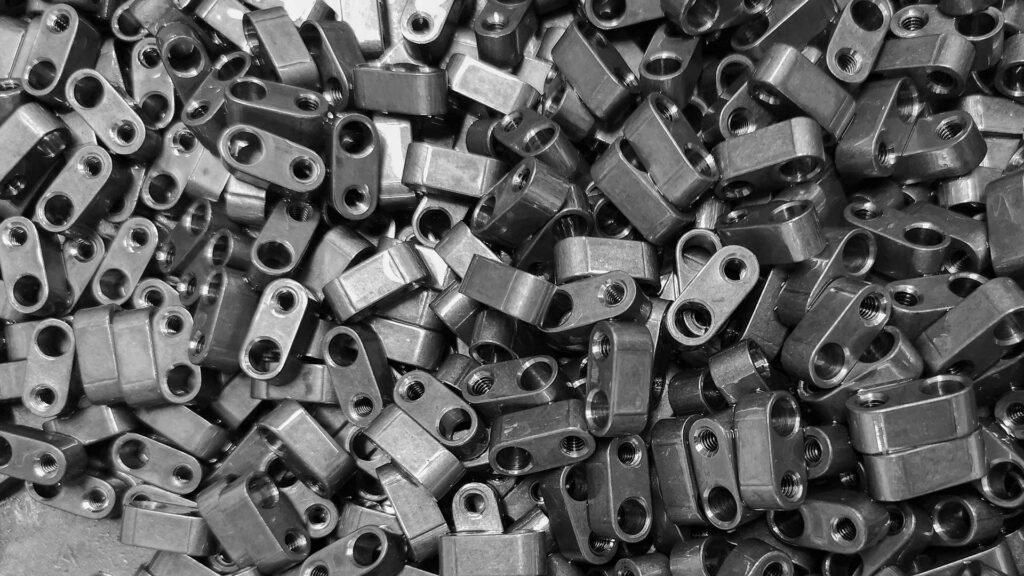
Keyed connections (see image) are commonly used today to create a fixed connection between shafts and hubs of heavy components such as pulleys, wheels, or couplings in large machinery — e.g. excavators or agricultural equipment. They are particularly suited for harsh conditions with alternating and shock-loaded torque. The forces are primarily transmitted by friction. If friction is overcome, the positive-locking effect of the key provides additional torque transmission.
Keyed connections wedge the shaft and hub together using keys with a slope of 1:100 and lateral play in the shaft and hub keyways. Thus, they form an intermediate type of connection between purely friction-locking and purely positive-locking designs.
Advantages: Even force distribution across the entire circumference, reduced wear due to multiple load-bearing contact surfaces, and reliable transmission of high and varying torques.
Disadvantages: Significantly more expensive, greater weakening of the shaft and hub, and increased notch effect.
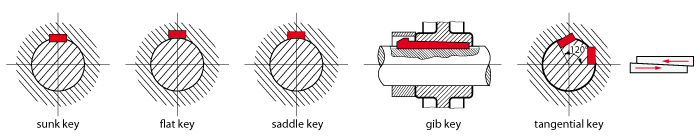
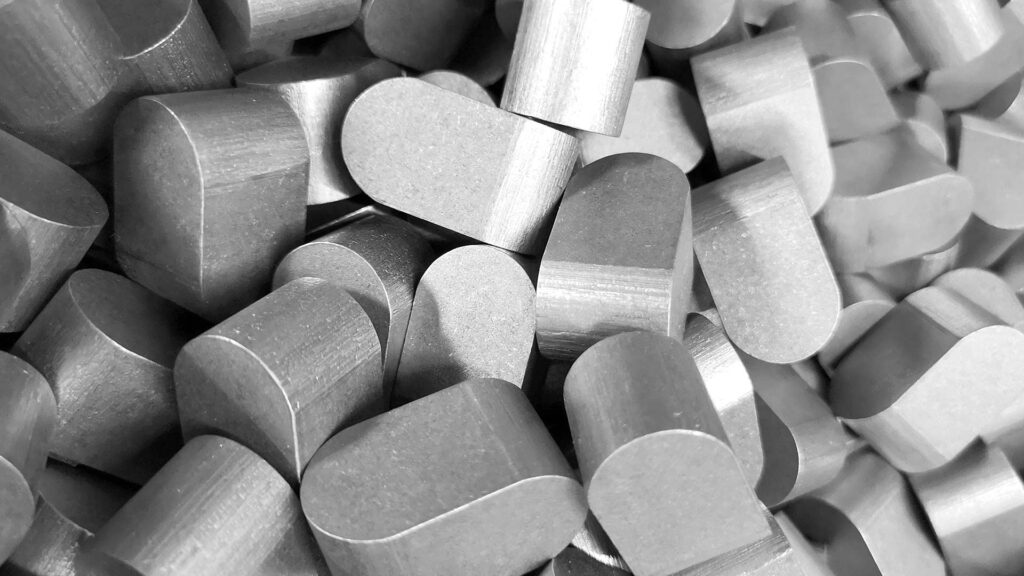
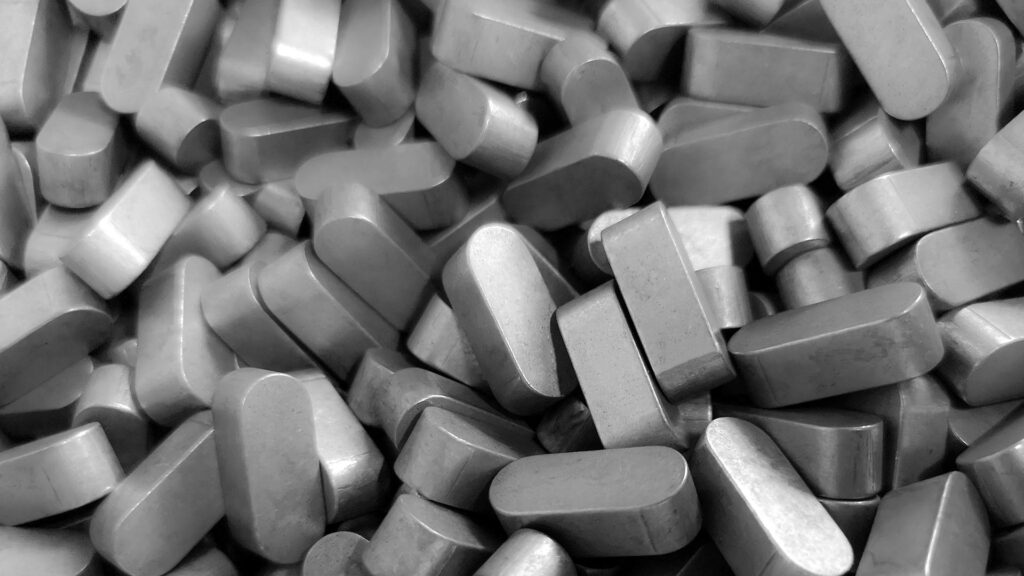
There are various types of keys, differing in shape and cross-section (see image below). These are standardized as follows:
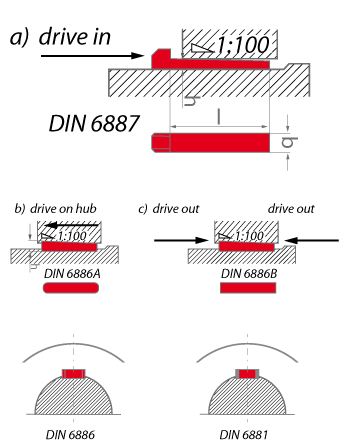
DIN 6881 (Gib head keys), DIN 6883 (Flat keys), DIN 6886, DIN 6884 (Feather keys with nose), and DIN 6889 (Gib head keys with nose).
Flat keys (DIN 6883 and 6884) offer very little positive-locking effect, but generate less notch stress compared to parallel keys.
Gib head keys (DIN 6881 and 6889) have a rounded bottom surface, allowing them to rest on the shaft diameter and transmit force via friction.
Tangential keys (DIN 268 and 271) are suitable for high and alternating torque loads. They are used in split hubs, e.g. flywheels, and are arranged tangentially around the shaft in pairs, offset by 120°.
Please complete the form below and we will help you as quickly as possible. The form is also available as a pdf file to download, complete and fax to us.
Contact
Contact form
Contact Details
Crummenerl GmbH (Office)
Bannewerthstr. 18
58840 Plettenberg
Germany
Crummenerl GmbH
(goods receiving / goods issue / truck access)
Bannewerthstr. 24c
58840 Plettenberg
Germany
Phone: +49 (0)2391 91796–0
Fax: +49 (0)2391 91796–30
E-Mail: in**@*************bh.de
Web: www.crummenerl-gmbh.de





Contact
Contact Form
Contact Details
Crummenerl GmbH (Office)
Bannewerthstr. 18
58840 Plettenberg
Germany
Crummenerl GmbH
(goods receiving / goods issue / truck access)
Bannewerthstr. 24c
58840 Plettenberg
Germany
Phone: +49 (0)2391 91796–0
Fax: +49 (0)2391 91796–30
E-Mail: in**@*************bh.de
Web: www.crummenerl-gmbh.de





